A new security vulnerability named “BrutePrint” has been uncovered in Android, HarmonyOS, and iOS devices, which poses a threat to fingerprint security and device control. Xuanwu Lab, Tencent, in collaboration with Zhejiang University, China, has published this research.
BrutePrint attacks exploit the method of trial and error to bypass codes, keys, or passwords, ultimately gaining unauthorized access to accounts, systems, or networks.
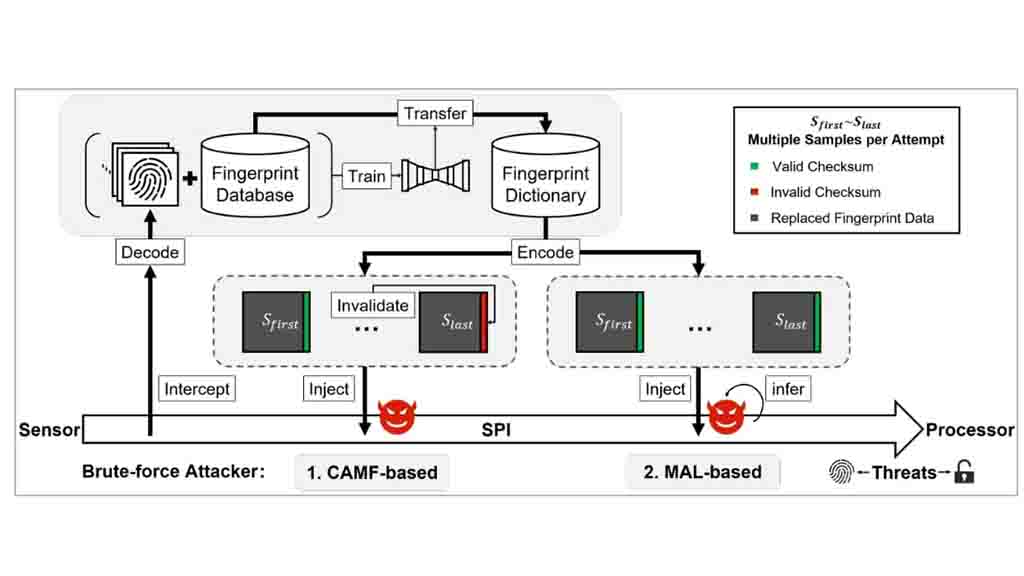
The researchers identified and exploited two zero-day vulnerabilities known as Cancel-After-Match-Fail (CAMF) and Match-After-Lock (MAL).
Additionally, they found that the biometric data stored on the serial peripheral interface (SPI) of the fingerprint sensor is not adequately protected.
This vulnerability opens the door for potential man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, enabling the interception of fingerprint images and subsequently compromising the device’s fingerprint security.
This discovery highlights the importance of addressing these vulnerabilities promptly to ensure the protection of user data and device integrity. It also emphasizes the need for robust security measures to safeguard against evolving threats in the digital landscape.
According to a research paper published, it has been revealed that ten commonly used smartphones have successfully executed an unlimited number of attempts to crack fingerprints on all Android and Huawei HarmonyOS devices. In addition, these devices were able to perform ten additional attempts on iOS devices.
This finding raises concerns about the effectiveness of fingerprint security measures on these platforms. The ability to carry out unlimited attempts significantly increases the risk of unauthorized access to devices, compromising the security and privacy of users.
It is crucial for device manufacturers and operating system developers to address these vulnerabilities promptly. Strengthening the security mechanisms surrounding fingerprint authentication is essential to ensure the protection of user data and prevent potential breaches.
Further research and development efforts are needed to enhance the resilience of biometric security systems, mitigating the risk posed by such attacks and maintaining user trust in these technologies.
BrutePrint:
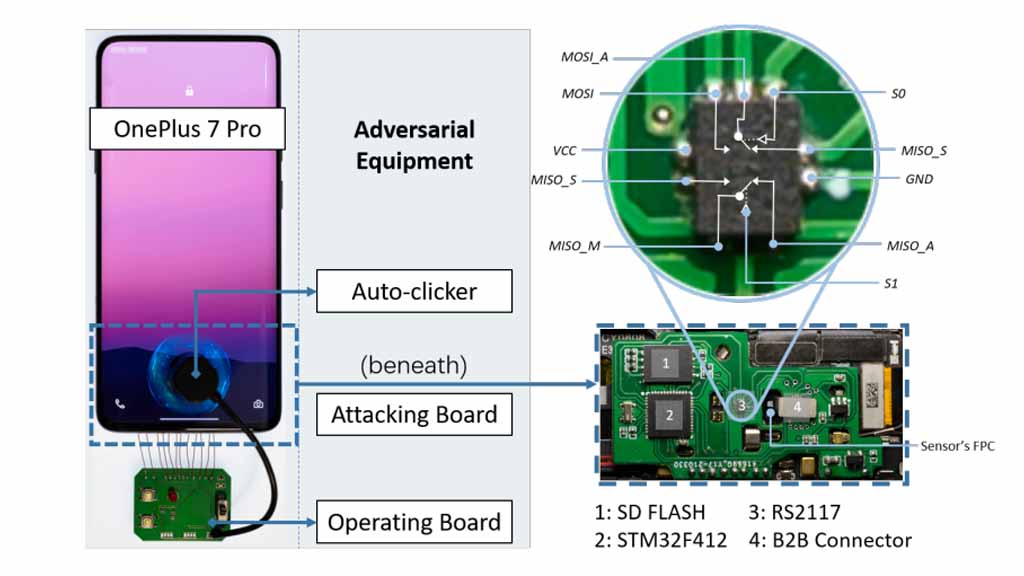
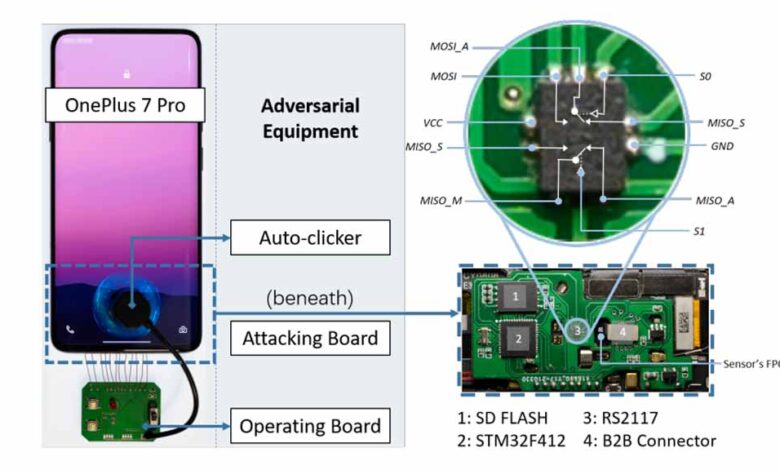
The BrutePrint attack concept involves continuously submitting fingerprint images to the targeted device until a match is found with the original fingerprint. It should be noted that attackers require physical access to the device in order to inject this vulnerability.
The research also highlights that obtaining fingerprint data for such attacks could involve accessing government databases or acquiring biometric data through other means. Interestingly, the study mentions the availability of a tool priced at $15 that facilitates the extraction of fingerprint data.
These findings emphasize the importance of safeguarding personal biometric information and implementing robust security measures. It is crucial for device manufacturers and software developers to continually enhance the security of fingerprint authentication systems, ensuring that they remain resilient against such attacks.
Furthermore, users should be aware of the potential risks associated with biometric authentication and take necessary precautions to protect their devices and personal data. This includes utilizing additional security measures, such as strong passcodes or two-factor authentication, to enhance the overall security posture of their devices.
The researchers have made an interesting breakthrough by exploiting the MAL zero-day vulnerability, which allows them to bypass the limit on the number of fingerprint unlock attempts. They have developed a system called “neural style transfer” that enables unlimited unlocking attempts on Android and HarmonyOS devices.
The system works by converting all fingerprint images in the database based on the specific type of sensor used in the target device. This conversion capability supports various types of fingerprint scanners, including capacitive, optical, ultra-thin, and ultrasonic scanners.
By leveraging this technique, the researchers have successfully demonstrated the ability to perform unlimited unlocking attempts, regardless of the type of fingerprint sensor used in the target device. This raises significant concerns regarding the security of fingerprint-based authentication systems.
The findings underscore the need for continuous improvement in fingerprint security measures and the development of robust countermeasures to mitigate the risk of such attacks.
Device manufacturers and software developers should work diligently to address these vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security of fingerprint recognition technology.
Additionally, users should remain vigilant and consider employing alternative security measures to supplement fingerprint authentication, especially in situations where highly sensitive data or access is involved.
10 Sample Devices:
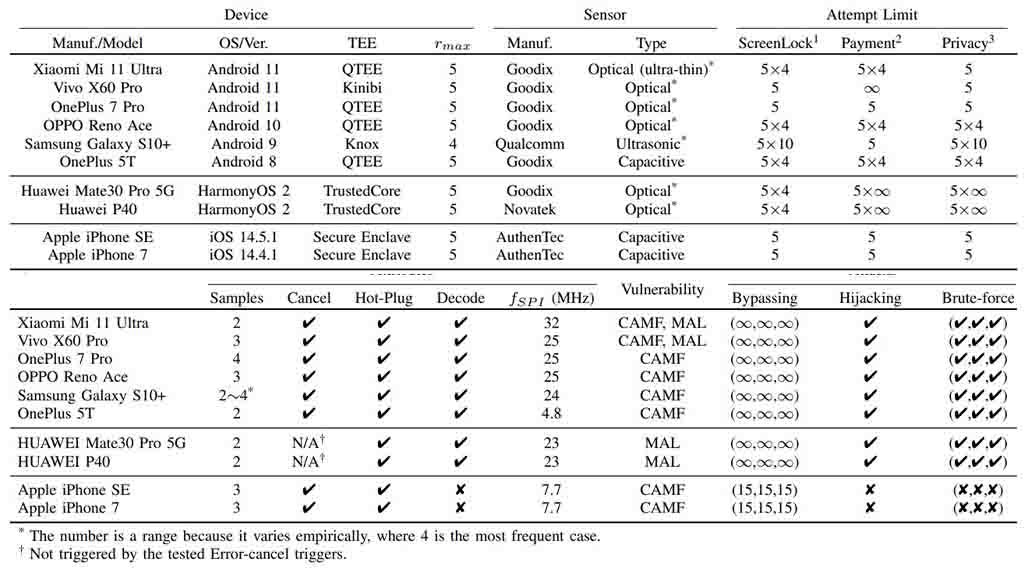
The researchers conducted their experiments using a total of 10 sample devices, including 6 Android smartphones, 2 HarmonyOS devices, and 2 Apple iPhones. The results of the tests revealed that all of the devices were susceptible to at least one vulnerability.
Notably, Android and HarmonyOS smartphones were found to be vulnerable to unlimited attacks through the BrutePrint method. This means that an attacker could make an infinite number of attempts to unlock these devices using fingerprint data.
On the other hand, it’s important to highlight that Apple iPhones that have upgraded to Face ID, starting from the iPhone X series, are not susceptible to this particular attack.
However, earlier iPhone models that rely on fingerprint recognition, such as Touch ID, could potentially be affected by the BrutePrint attack.
These findings underline the significance of regular security updates and advancements in biometric authentication technology.
Manufacturers should continue to enhance the security features of their devices to protect against evolving attack methods. Users of older iPhone models should be cautious and consider additional security measures to safeguard their devices and personal information.
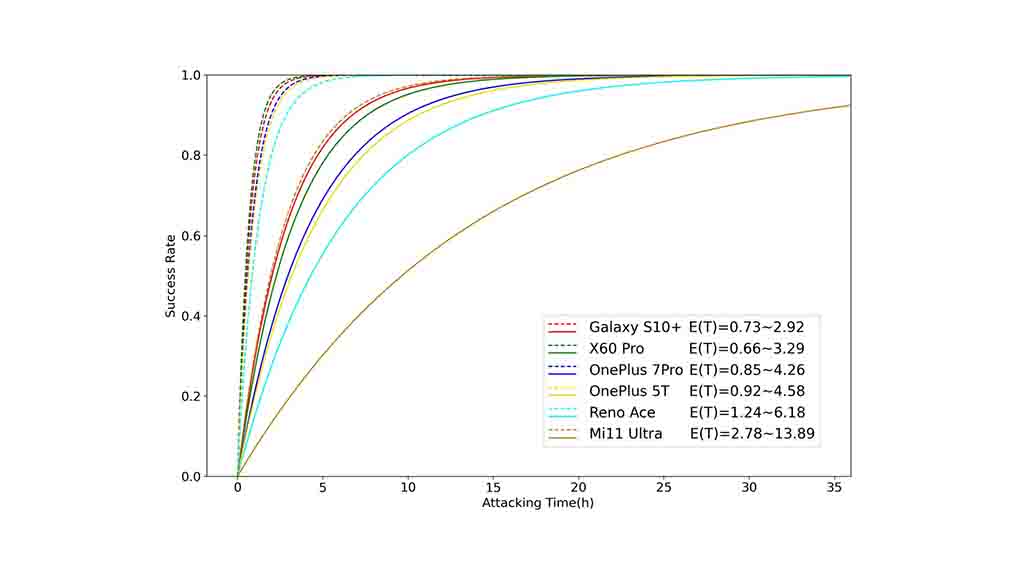
The research findings indicate that the time needed to successfully breach a phone using the BrutePrint attack varies between 2.9 to 13.9 hours. This duration represents the time it takes for the attacker to perform numerous fingerprint image submissions until a match is found with the original fingerprint.
However, it is worth noting that if the targeted phone has multiple registered fingerprints, the break-in time is significantly reduced. In such cases, the time required to breach the device ranges from 0.66 to 2.78 hours. This implies that having multiple registered fingerprints on the device can expedite the success of the BrutePrint attack.
These timeframes serve as a reminder of the importance of implementing strong security measures and regularly updating devices to protect against emerging vulnerabilities and attack techniques.
It is crucial for users to stay vigilant and take necessary precautions to safeguard their personal data and devices from potential unauthorized access.
To summarize, the BrutePrint attack is not an instant threat that users should be overly concerned about in their day-to-day activities. The attack requires physical access to the targeted device, whether it is running Android, HarmonyOS, or an earlier version of iOS.
While the attack process itself can be time-consuming, taking several hours to break into the device, it is important to note that this technique represents an advanced method for bypassing fingerprint authentication.
As technology evolves, it is crucial to remain cautious and aware of potential security vulnerabilities.
Users should exercise caution when handing their devices to individuals they do not trust or who may have malicious intentions to gain unauthorized access to personal data.
By maintaining control over their devices and implementing additional security measures such as passcodes, strong passwords, or utilizing more advanced authentication methods like facial recognition or two-factor authentication, users can further protect themselves from potential security breaches.
It is always advisable to stay informed about the latest security developments and follow best practices to ensure the privacy and security of personal data.