
As I take a walk down memory lane, I am reminded of the remarkable journey that Android, the world’s most popular mobile operating system, has taken since its inception.
Each version of Android brought new features, enhanced performance, and innovative technologies, shaping the way we interact with our smartphones.
The founder of Android, Andy Rubin, is a prominent figure in the world of technology and innovation. Born on June 22, 1963, in Chappaqua, New York, Rubin’s passion for computer programming and technology began at a young age. He attended Utica College, where he earned a degree in computer science.
Rubin’s career in the tech industry took off when he co-founded Danger, Inc., a company known for developing the Sidekick smartphone.
This venture laid the foundation for his future success in the mobile industry. In 2003, Rubin founded Android Inc., a company focused on creating an open-source operating system for mobile devices.
Under Rubin’s leadership, Android quickly gained recognition and popularity. In 2005, Google acquired Android Inc., and Rubin continued to work on the development of the Android operating system as a key member of the Google team. His vision was to create a flexible and customizable platform that could revolutionize the mobile industry.
Rubin’s efforts paid off when the first commercially available Android device, the HTC Dream (also known as the T-Mobile G1), was launched in 2008.
Since then, Android has become the most widely used mobile operating system globally, powering billions of devices around the world.
Rubin’s contributions to the tech industry go beyond Android. He is also known for his work on the creation of the Essential Phone, a high-end smartphone that aimed to provide a pure Android experience.
Despite leaving Google in 2014, Rubin’s impact on the mobile industry and his role in shaping Android’s success cannot be overstated.
His innovative ideas and dedication to creating an open ecosystem have transformed the way we interact with our smartphones and paved the way for a new era of mobile technology.
In this article, I will delve into the evolution of Android, exploring the key highlights and advancements in each version, from its humble beginnings to its current state as a powerhouse in the mobile industry.
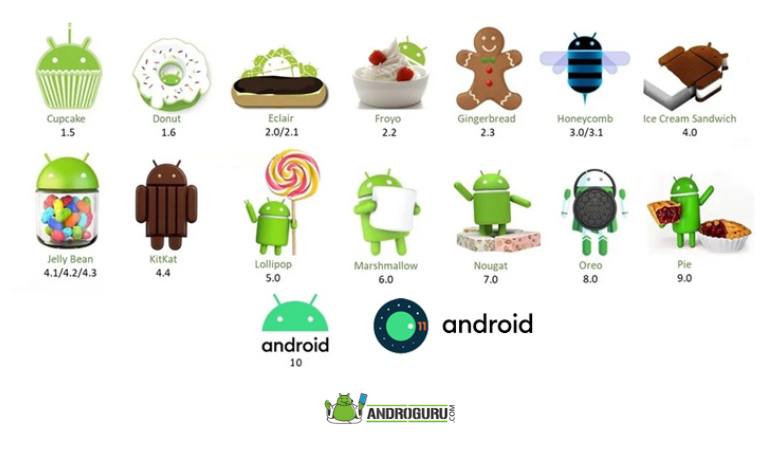
- Android 1.0 – The Birth of a Revolution:
Android 1.0 marked the beginning of the Android era, introducing a user-friendly interface and essential features like Gmail, Google Maps, and the Android Market (now known as Google Play Store). It laid the foundation for the seamless integration of Google services and set the stage for Android’s exponential growth.
- Android 1.5 Cupcake – Sweetness and Enhanced Features:
Cupcake brought numerous improvements, including an on-screen keyboard, support for widgets, video recording, and the ability to upload videos to YouTube. It was a significant step forward in terms of user experience and expanded the possibilities for developers to create innovative applications.
- Android 1.6 Donut – Refining the Experience:
Donut focused on optimizing performance and introducing features like speech-to-text capabilities, improved camera functionalities, and expanded search capabilities. It enhanced the overall usability of Android devices and provided a glimpse of the platform’s potential.
- Android 2.0/2.1 Eclair – A Taste of Multitasking and Voice Navigation:
Eclair brought multitasking capabilities, allowing users to switch between applications seamlessly. It also introduced live wallpapers, improved camera features, and voice-guided turn-by-turn navigation. Eclair revolutionized the Android experience and solidified its position as a formidable competitor in the mobile market.
- Android 2.2 Froyo – Speed and Optimization:
Froyo focused on speed and performance enhancements, introducing JIT compilation for improved application execution.
It also brought Wi-Fi hotspot capabilities, Adobe Flash support, and the ability to install applications on external storage. Froyo marked a significant leap forward in terms of functionality and performance.
- Android 2.3 Gingerbread – Polishing the Experience:
Gingerbread refined the user interface with a more polished and intuitive design. It introduced NFC support, improved copy-paste functionality, and enhanced gaming capabilities with the addition of a dedicated gaming framework. Gingerbread laid the groundwork for the future advancements of the Android platform.
- Android 3.0/3.1/3.2 Honeycomb – Optimized for Tablets:
Honeycomb was a milestone release, specifically tailored for tablets. It introduced a tablet-optimized user interface, multi-pane layout, and enhanced multitasking. Honeycomb showcased Android’s adaptability to different form factors and its commitment to providing a tailored experience for users.
- Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich – A Unified Experience:
Ice Cream Sandwich brought a unified experience across smartphones and tablets, introducing a visually appealing design, enhanced multitasking, and refined notifications.
It also introduced Face Unlock, a feature that used facial recognition for device authentication. Ice Cream Sandwich set the stage for a seamless user experience across various devices.
- Android 4.1/4.2/4.3 Jelly Bean – Smoother Performance and Enhanced Features:
Jelly Bean focused on improving performance with Project Butter, which brought smoother animations and responsiveness. It also introduced features like Google Now, expandable notifications, and support for multiple user accounts on tablets. Jelly Bean solidified Android’s position as a powerful and feature-rich operating system.
- Android 4.4 KitKat – Optimization for All:
KitKat aimed to optimize Android for devices with lower hardware specifications, making it accessible to a broader range of users. It introduced a new immersive mode, improved Google Now integration, and enhanced security features. KitKat showcased Android’s commitment to inclusivity and its ability to adapt to varying device capabilities.
- Android 5.0/5.1 Lollipop – Material Design and Enhanced Performance:
Lollipop brought a visually stunning material design, introducing a more intuitive and consistent user interface. It also enhanced performance with the ART runtime, improved battery life, and introduced features like Smart Lock and multiple device compatibility with Android Wear. Lollipop represented a significant leap forward in terms of design and performance.
- Android 6.0 Marshmallow – Advanced Control and Security:
Marshmallow focused on giving users more control over their devices with features like app permissions and a more efficient power-saving mode. It also introduced Google Now on Tap, which provided contextual information within apps. Marshmallow emphasized user privacy, security, and overall device optimization.
- Android 7.0/7.1 Nougat – Seamless Productivity and VR Support:
Nougat introduced split-screen multitasking, enhanced notification management, and improved battery optimization. It also brought support for Daydream, Google’s virtual reality platform, and introduced the Vulkan Graphics API for advanced gaming experiences. Nougat expanded Android’s capabilities and provided a more immersive user experience.
- Android 8.0/8.1 Oreo – Speed, Efficiency, and Picture-in-Picture:
Oreo focused on speed and efficiency with features like Project Treble for faster updates and improved battery life through background limits.
It also introduced picture-in-picture mode, notification dots, and autofill for seamless user experiences. Oreo emphasized Android’s commitment to delivering enhanced performance and productivity.
- Android 9 Pie – Adaptive Intelligence and Digital Wellbeing:
Pie brought adaptive features with Adaptive Battery and Adaptive Brightness, utilizing AI to optimize device performance.
It introduced Digital Wellbeing tools to help users manage their smartphone usage. Pie emphasized Android’s dedication to leveraging AI and ML for a personalized and balanced user experience.
- Android 10 – Gestures and Privacy Controls:
Android 10 introduced gesture-based navigation, providing a more intuitive way to interact with devices. It also enhanced privacy with features like scoped storage and location controls. Android 10 emphasized user-centric design and privacy enhancements.
- Android 11 – Conversations and Smart Home Controls:
Android 11 focused on improving communication with features like conversation notifications, dedicated conversation sections, and chat bubbles. It also introduced enhanced smart home controls, allowing users to control their smart devices directly from the notification shade. Android 11 emphasized seamless communication and expanded integration with the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Android 12 – Material You and Privacy Enhancements:
Android 12 introduced the revolutionary Material You design language, offering a more personalized and dynamic user interface.
It also enhanced privacy with features like approximate location permissions and the Privacy Dashboard, giving users more control over their data. Android 12 showcased Google’s commitment to user customization and privacy protection.
- Android 13 – Enhanced Performance and Connectivity:
Android 13 is expected to bring further performance improvements, optimizing resource usage and enhancing overall device responsiveness. It may also introduce advancements in connectivity, leveraging technologies like 5G and Wi-Fi 6 for faster and more stable connections. Android 13 will likely continue the trend of seamless user experiences and cutting-edge technologies.
- Android 14 and Beyond – The Future Unveiled:
Looking beyond Android 13, the future of Android holds immense potential. With the integration of AI, ML, DL, robotics, and other emerging technologies, Android is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with our devices.
We can expect more intelligent and context-aware experiences, enhanced security and privacy features, and further advancements in connectivity and device performance.
The possibilities are limitless as Android continues to evolve and adapt to the ever-changing needs of users.
The evolution of Android has been nothing short of extraordinary. Each version has brought significant improvements and innovative features, transforming the mobile experience for millions of users worldwide.
From its early stages as a simple operating system to its current state as a sophisticated and versatile platform, Android has continuously pushed the boundaries of what’s possible. As we look ahead to the future, it is evident that Android’s integration with AI, ML, DL, robotics, and other technologies will redefine the way we use our smartphones and propel us into a new era of digital innovation.
Android’s journey is a testament to its commitment to delivering excellence and staying at the forefront of mobile technology.












10 Comments